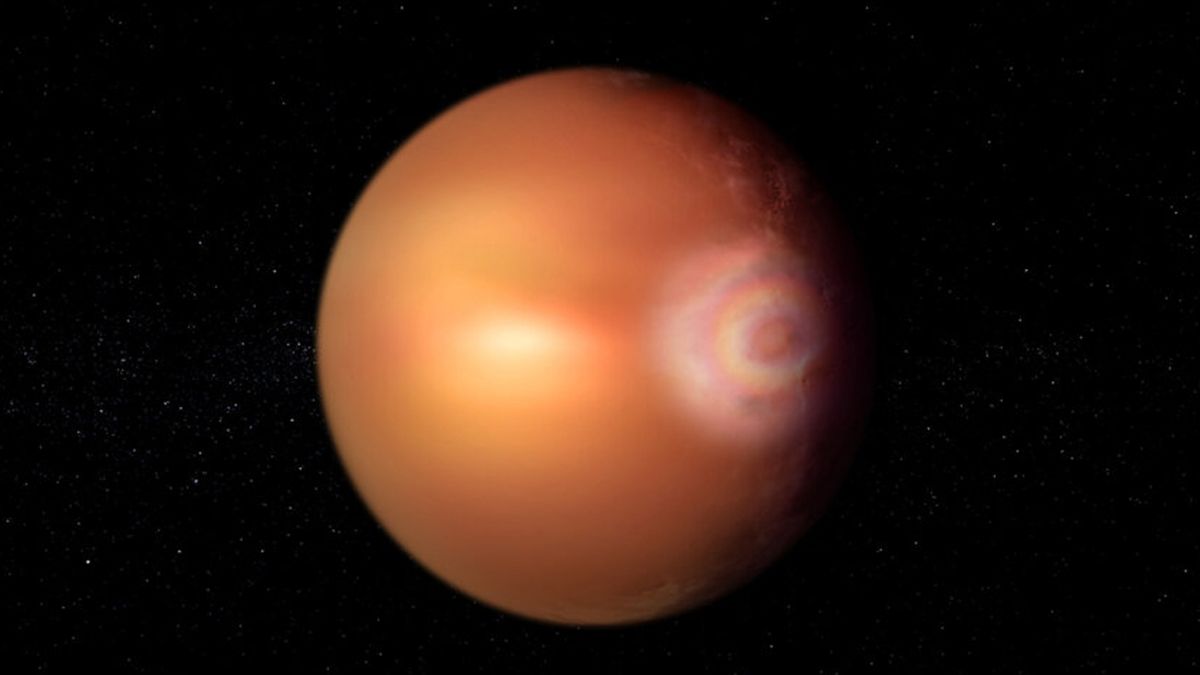
Astronomers believe they have discovered an extremely rare, luminous phenomenon known as “glory” in the hellish atmosphere of a distant exoplanet. If this discovery is confirmed, it will be the first time one of these rainbow-colored light displays has been observed outside the solar system.
The exoplanet, WASP-76 b, is located about 637 light-years from Earth. It was first discovered in 2013 by the Wide-Angle Planet Search Project (WASP), which searches for planets as they pass between or transit between their parent star and Earth.
Exoplanet – which may be The dismantling of a smaller, Mercury-sized neighbor in the past – About 90% of the mass Jupiter But about twice the width. It is unusually close to its parent star, orbiting its star 20 times closer Mercury Orbits the sun. As a result, WASP-76 b takes only 1.8 days to complete one trip around its star.
In 2020, researchers discovered that the planet is tidally locked, meaning one side of it always faces its parent star, just like Earth. the moon Facing the ground. As a result, the temperature of the exoplanet's sunlit side is about 4,350 degrees Fahrenheit (2,400 degrees Celsius), while its dark side is slightly cooler. Researchers believe that because of this subtle temperature difference, minerals such as iron can evaporate on the light side and then condense into rain on the dark side.
In a new study published April 5 in the journal Astronomy and astrophysicsThe researchers examined new data on WASP-76 b collected by multiple spacecraft, including the European Space Agency's (ESA) Exoplanet Characterization Satellite and NASA's Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite. This analysis revealed a “bright spot” of light coming from the eastern tip of the exoplanet, along the boundary where the planet's perpetual day and night meet.
Researchers believe that this bright spot could serve as “glory.” This rare optical phenomenon, when seen on Earth, usually consists of concentric rainbow rings forming a giant circle.
Related: 10 extreme exoplanets that are out of this world
On the ground, Glories are formed When sunlight is squeezed through tiny holes between water molecules in clouds or fog, bending the light and splitting it into individual wavelengths. This is similar to How does a rainbow work?Except with Majad, light bends by diffraction, which is when light bends around an obstacle, rather than refraction, or when light bends as it passes through different media.
“It requires very strange conditions,” said the study's lead author Olivier DemangioneAn astronomer at the Portuguese Institute of Astrophysics and Space Sciences, A statement. “First, we need atmospheric molecules that are perfectly spherical, perfectly uniform and stable enough to observe them over a long period.” He added that the observer must be in exactly the right direction to be able to see the diffracted light.
However, it is possible, if similar conditions exist, for the impact to occur on other planets. We have already seen this phenomenon elsewhere in the solar system, on the planet Venus, according to the American “space” website. European Space Agency.
Researchers aren't sure exactly how Glory formed on WASP-76 b. But given that the bright spot was visible over several years, the medium that diffracts the light is likely more stable than the water vapor in our planet's atmosphere.
However, the glory theory is based on an “incredibly faint signal,” so it is not confirmed. Matthew standing upAn exoplanet scientist at the European Space Agency who was not involved in the study said in the statement.
“Additional evidence is needed to say conclusively that this intriguing ‘extra light’ is a rare glory.” Theresa LoftingerAn astrophysicist at the European Space Agency who was not involved in the study said in the statement. We will likely need more powerful tools, such as those found in James Webb Space TelescopeShe added: To obtain this evidence.
If it works, researchers could use the data to look for more extrasolar examples of these light displays in the atmospheres of other exoplanets to learn more about this puzzling phenomenon.




More Stories
Boeing May Not Be Able to Operate Starliner Before Space Station Is Destroyed
Prehistoric sea cow eaten by crocodile and shark, fossils say
UNC student to become youngest woman to cross space on Blue Origin